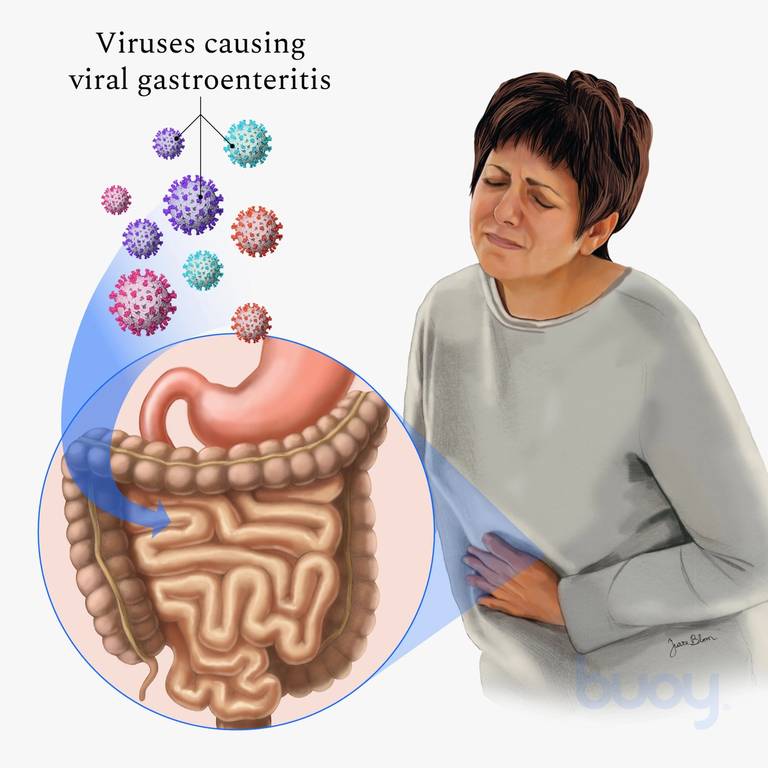
Gastroenteritis, commonly known as stomach flu or stomach bug, is inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract that results in symptoms such as diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and sometimes fever. While typically caused by viral infections, bacteria, parasites, or even certain medications and foodborne illnesses can also trigger gastroenteritis. Recognizing the signs and understanding effective treatments are crucial for managing this condition.
Key Signs and Symptoms of Gastroenteritis
- Diarrhea:
- Watery or loose stools that occur frequently, often accompanied by urgency.
- Vomiting:
- Forceful expulsion of stomach contents through the mouth, which may be persistent.
- Abdominal Pain:
- Cramping or discomfort in the abdominal region, varying in intensity.
- Nausea:
- Feeling of queasiness or an urge to vomit, commonly experienced with gastroenteritis.
- Fever:
- Elevated body temperature, indicating the body’s immune response to infection.
- Dehydration:
- Symptoms may include dry mouth, decreased urine output, dizziness, and fatigue, particularly in severe cases or prolonged illness.
Causes of Gastroenteritis
- Viral Infections:
- Rotavirus and norovirus are common viral causes, particularly in children and adults, respectively.
- Bacterial Infections:
- Bacteria such as Salmonella, Escherichia coli (E. coli), and Campylobacter can cause gastroenteritis through contaminated food or water.
- Parasitic Infections:
- Parasites like Giardia lamblia and Cryptosporidium can lead to gastroenteritis, often due to waterborne transmission.
- Toxins and Chemicals:
- Certain toxins and chemicals, including those found in contaminated food or beverages, can trigger gastroenteritis symptoms.
- Medications:
- Some medications, especially antibiotics or those that affect gastrointestinal motility, can cause gastroenteritis-like symptoms as a side effect.
Treatment Options for Gastroenteritis
- Fluid Replacement:
- Rehydration is crucial to replace fluids and electrolytes lost through diarrhea and vomiting. Oral rehydration solutions (ORS) or intravenous (IV) fluids may be necessary in severe cases.
- Symptomatic Relief:
- Over-the-counter medications such as anti-diarrheals (e.g., loperamide) and anti-emetics (e.g., ondansetron) can help manage symptoms like diarrhea and vomiting.
- Rest and Recovery:
- Adequate rest and avoiding solid foods for a period can aid in recovery and allow the gastrointestinal tract to heal.
- Natural Remedies:
- Herbal teas (e.g., chamomile or ginger tea) and probiotics (e.g., yogurt with live cultures) may help restore gut flora and alleviate symptoms naturally.
- Medical Evaluation:
- Seek medical attention if symptoms persist for more than a few days, if there are signs of dehydration, or if there is blood in vomit or stool.
Natural Approaches to Supporting Digestive Health
Wellhealthorganic.com promotes natural and organic approaches to health, including digestive wellness. Here are some tips aligned with their philosophy:
- Healthy Diet:
- Consume a balanced diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins to support digestive function.
- Hydration:
- Drink plenty of water and herbal teas to maintain hydration, especially during episodes of gastroenteritis.
- Probiotics:
- Incorporate probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables to promote a healthy gut microbiome.
- Gentle Herbal Remedies:
- Use gentle herbs like peppermint, chamomile, and ginger to soothe digestive discomfort and reduce inflammation.
- Avoid Irritants:
- Limit intake of spicy foods, caffeine, alcohol, and processed foods that may exacerbate gastrointestinal symptoms.
Spotting Gastroenteritis: The Basics
Gastroenteritis encompasses a range of symptoms, often leading to discomfort and distress. Recognizing these signs is the first step towards seeking appropriate medical attention.
WELLHEALTHORGANIC.COM : KEY SIGNS OF GASTROENTERITIS
Gastroenteritis manifests through various indicators, including:
- Nausea and Vomiting: Persistent feelings of queasiness, accompanied by vomiting, are common symptoms of gastroenteritis. These manifestations often result from the body’s efforts to expel harmful pathogens.
- Diarrhea: Loose, watery stools are hallmark symptoms of gastroenteritis, indicating inflammation and irritation within the gastrointestinal tract.
- Abdominal Pain and Cramping: Intense abdominal discomfort, characterized by cramping or aching sensations, is prevalent in gastroenteritis cases. This discomfort may vary in severity and duration.
- Fever: Elevated body temperature is a typical response to infection, signaling the immune system’s efforts to combat invading pathogens. In gastroenteritis, fever often accompanies other symptoms, indicating a systemic response to infection.
- Dehydration: Excessive fluid loss through diarrhea and vomiting can lead to dehydration, a potentially serious complication of gastroenteritis. Symptoms of dehydration include dry mouth, decreased urine output, and lightheadedness.
Understanding The Onset: Causes And Risk Factors
Gastroenteritis can stem from various causes, ranging from viral and bacterial infections to dietary indiscretions and environmental factors.
COMMON CULPRITS
- Viral Infections: Rotavirus and norovirus are among the leading viral agents responsible for gastroenteritis outbreaks, particularly in crowded or communal settings.
- Bacterial Pathogens: Bacteria such as Escherichia coli (E. coli), Salmonella, and Campylobacter are notorious for causing bacterial gastroenteritis, often transmitted through contaminated food or water.
- Parasitic Infections: Parasites like Giardia lamblia and Cryptosporidium can trigger gastroenteritis, typically through ingestion of contaminated food or water sources.
RISK FACTORS
Certain factors increase the susceptibility to gastroenteritis, including:
- Age: Infants, young children, and older adults are more vulnerable to gastroenteritis due to weaker immune systems and reduced resilience to infections.
- Weakened Immunity: Individuals with compromised immune function, such as those with chronic illnesses or immunodeficiency disorders, face a higher risk of gastroenteritis.
- Environmental Conditions: Poor sanitation, inadequate hygiene practices, and close contact with infected individuals contribute to the spread of gastroenteritis in communities.
Seeking Relief: Management And Treatment
Managing gastroenteritis involves a multifaceted approach aimed at alleviating symptoms, preventing complications, and promoting recovery.
HYDRATION AND ELECTROLYTE BALANCE
- Oral Rehydration Therapy: Consuming oral rehydration solutions helps replenish lost fluids and electrolytes, aiding in the prevention of dehydration.
- Fluid Intake: Encouraging adequate fluid intake, including water, clear broths, and electrolyte-rich beverages, supports hydration and facilitates recovery.
DIETARY MODIFICATIONS
- BRAT Diet: Following a diet comprising bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast can help soothe the stomach and provide easily digestible nutrients during bouts of gastroenteritis.
- Avoidance of Irritants: Steering clear of spicy, fatty, or overly processed foods minimizes gastrointestinal distress and promotes healing.
MEDICATIONS AND SYMPTOMATIC RELIEF
- Antidiarrheal Medications: Over-the-counter antidiarrheal agents may offer temporary relief from diarrhea, although they should be used judiciously and under medical guidance.
- Analgesics: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or acetaminophen can help alleviate fever and discomfort associated with gastroenteritis.
Prevention Strategies: Safeguarding Gut Health
Preventing gastroenteritis entails adopting proactive measures to reduce the risk of infection and transmission.
- Hand Hygiene: Practicing frequent handwashing with soap and water, especially before meals and after using the restroom, is critical for preventing the spread of gastroenteritis-causing pathogens.
- Food Safety: Adhering to proper food handling, storage, and preparation practices minimizes the risk of foodborne illnesses, including gastroenteritis.
- Vaccination: Vaccination against specific pathogens, such as rotavirus, can significantly reduce the incidence and severity of gastroenteritis, particularly in young children.
Conclusion
Understanding the key signs, causes, and treatment options for gastroenteritis is essential for effectively managing this common condition. By recognizing symptoms early and adopting appropriate treatments, individuals can minimize discomfort and aid recovery. Natural and organic approaches, as advocated by Wellhealthorganic.com, offer additional options for supporting digestive health and overall wellness.